Fermentation has been a vital part of human food practices for centuries, creating some of the most beloved foods and drinks we consume today. From yogurt and kimchi to kombucha and sauerkraut, fermented foods have gained popularity not just for their distinctive flavors, but for their impressive health benefits. One of the most notable benefits of fermented foods is their ability to promote gut health through the introduction of beneficial bacteria, known as probiotics. This article explores the health benefits of fermented foods and their positive impact on our digestive system and overall well-being.

What Is Fermentation?
Fermentation is a natural metabolic process in which microorganisms like bacteria, yeast, or molds break down sugars in food. This process not only preserves food but also enhances its nutritional content. During fermentation, beneficial bacteria (probiotics) are produced, which can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome—the collection of bacteria and microorganisms that live in our digestive system. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for maintaining digestive health, supporting immunity, and even influencing mood and mental health.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
- Improved Digestion and Gut Health
The primary benefit of consuming fermented foods is the positive effect they have on the digestive system. Probiotics introduced through fermented foods can help restore the natural balance of gut bacteria, which may be disrupted by factors like antibiotics, poor diet, or stress. This restoration helps with digestion and can reduce symptoms of digestive disorders like bloating, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Fermented foods are often rich in fiber and enzymes, both of which aid in digestion and make it easier for the body to absorb nutrients. They can also support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, leading to a healthier and more efficient digestive system.
- Boosting Immune Function
A significant portion of the immune system resides in the gut, so maintaining a healthy gut microbiome can directly impact overall immune function. Probiotic-rich foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt help reinforce the gut’s ability to protect the body from harmful pathogens, bacteria, and viruses. Studies have shown that probiotics can enhance immune responses, reduce the risk of infections, and improve the body’s ability to fight off illness.
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Fermented foods can increase the bioavailability of nutrients, meaning they make it easier for your body to absorb and utilize the nutrients in food. For example, the fermentation process can break down certain compounds in food that may inhibit nutrient absorption, such as phytates. As a result, consuming fermented foods can improve the absorption of essential vitamins and minerals, like iron, zinc, and B vitamins, leading to improved overall health.
- Support for Mental Health
The connection between the gut and the brain is known as the “gut-brain axis,” and recent research suggests that the health of our gut microbiome can influence mood, stress levels, and cognitive function. Probiotic foods have been linked to a reduction in symptoms of depression and anxiety, likely due to their positive effect on gut bacteria. Gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which plays a key role in regulating mood. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, fermented foods may have a role in supporting mental health.
- Detoxification and Antioxidant Properties
Fermented foods contain antioxidants, which help protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation. These antioxidants are produced as a byproduct of fermentation and can help detoxify the body by neutralizing free radicals, reducing inflammation, and supporting liver function. Foods like kimchi, kefir, and miso are particularly known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Weight Management
Some studies suggest that probiotics can help with weight management by influencing the gut microbiome in a way that supports metabolism. Fermented foods may help regulate hormones related to hunger and satiety, reducing cravings and promoting a feeling of fullness. Additionally, certain probiotics may help the body burn fat more efficiently. However, more research is needed to fully understand the connection between probiotics and weight management.
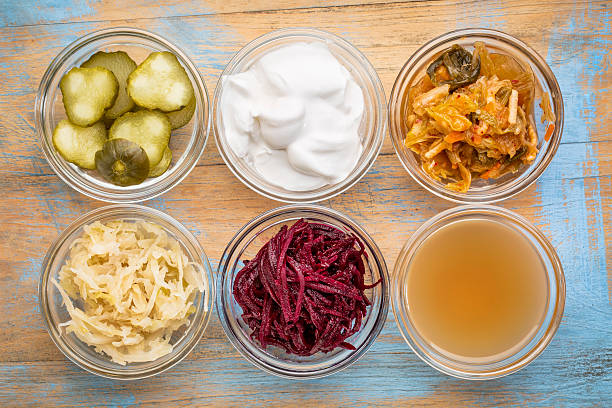

Popular Fermented Foods and Their Benefits
- Yogurt
Yogurt is one of the most widely consumed fermented foods. It’s made by fermenting milk with specific bacterial cultures, which turn lactose (milk sugar) into lactic acid. The live and active cultures in yogurt, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are beneficial probiotics that can improve digestion, boost immunity, and support gut health. Additionally, yogurt is rich in calcium, protein, and vitamins, making it a nutritious addition to a balanced diet.
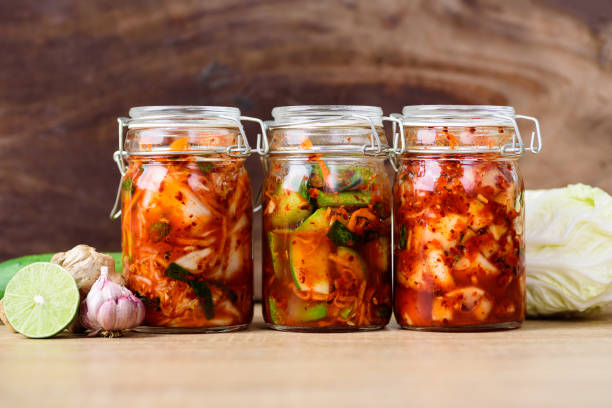
- Kimchi
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, typically napa cabbage and radishes, seasoned with chili pepper, garlic, and other spices. Like other fermented foods, kimchi is rich in probiotics, which help support a healthy digestive system. Studies have also suggested that kimchi may have additional health benefits, including improving heart health, reducing inflammation, and supporting immune function.
- Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea made by adding a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) to sweetened tea. The fermentation process produces a drink rich in probiotics, organic acids, and antioxidants. Kombucha is praised for its potential to improve digestion, detoxify the body, and support liver health. It also contains small amounts of caffeine and can provide a mild energy boost without the jitters associated with coffee.
- Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut, a fermented cabbage dish commonly associated with German cuisine, is another popular probiotic-rich food. Made by fermenting finely shredded cabbage with salt, sauerkraut is a potent source of beneficial bacteria that help support digestive health. It’s also low in calories, rich in fiber, and packed with vitamins like vitamin C and K.
- Miso
Miso, a staple in Japanese cuisine, is made by fermenting soybeans with salt and a specific mold called Aspergillus oryzae. This fermentation process produces a rich, savory paste used to make miso soup and other dishes. Miso is a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, and like other fermented foods, it contains probiotics that can improve gut health and digestion.
How to Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Adding fermented foods to your diet doesn’t require major changes—small, gradual additions can yield big health benefits. Here are some simple ways to incorporate more fermented foods into your meals:
- Add a serving of yogurt to your breakfast, topping it with fruit, nuts, or seeds.
- Include a side of kimchi or sauerkraut with your main meals for an added probiotic boost.
- Drink a small glass of kombucha as a refreshing beverage or mix it into smoothies.
- Use miso paste as a flavor enhancer in soups, sauces, and dressings.
- Experiment with fermented vegetables by making your own pickles or fermented carrots at home.
Conclusion: A Gut-Friendly Future
The power of fermentation extends far beyond its rich flavors and culinary traditions. By incorporating fermented foods into your diet, you can improve gut health, boost your immune system, and even support mental well-being. As more people become aware of the benefits of probiotics and gut health, the popularity of fermented foods is likely to continue growing, leading to a healthier, more vibrant approach to eating. Whether you’re sipping kombucha, snacking on yogurt, or enjoying a bowl of kimchi, fermented foods offer a tasty way to nourish both your body and your microbiome.